Everyone knows the situation where you can’t log into a system because you have forgotten the password. The following article explains how to reset the password and regain access to VMware vSphere 6.5 core components including vCenter, SSO and ESXi Hosts.

- Reset vCenter Server Appliance 6.5 root password
- Reset SSO Administrator Password (vCenter Server Appliance 6.5)
- Reset ESXi root password with Host Profiles
- Gain Administrative ESXi access with an Active Directory
- Reset ESXi root password (Linux Live CD)
Reset vCenter Server Appliance 6.5 root password
The following method provides steps to recover the vCenter Server Appliance (vCSA) root password. The process is slightly different compared to previous versions as the OS has been changed to PhotonOS. The method is officially supported by VMware and documented in KB2147144.
- Take a snapshot of the vCSA to be able to rollback in case of any problems during password recovery.
- Connect to the ESXi Host that runs the vCSA and open a remote console.
- Reboot the vCSA
- Press e immediately after the system starts (When the PhotonOS screen shows up)
- Append rw init=/bin/bash to the line starting with linux
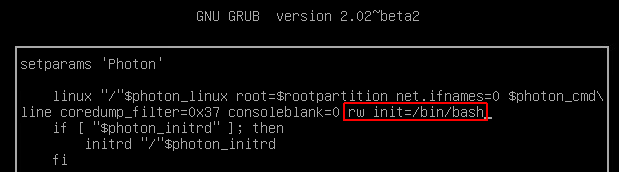
- Press F10 to boot
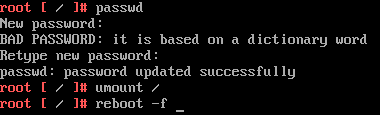
- In the command prompt, enter passwd and enter a new root password twice
- Enter umount / to unmount the root filesystem
- Reboot the vCSA by running the command reboot -f
- Verify that you can log in with the new root password and delete the snapshot created in step 1.
Reset SSO Administrator Password (vCenter Server Appliance 6.5)
The following method provides steps to recover the SSO administrator password on a vCenter Server Appliance (vCSA). The method is officially supported by VMware and documented in KB2146224.
- Log in to the vCSA using SSH as root
- Enter shell to start the bash shell
- Identify the SSO Domain Name (Default is vsphere.local)
# /usr/lib/vmware-vmafd/bin/vmafd-cli get-domain-name --server-name localhost

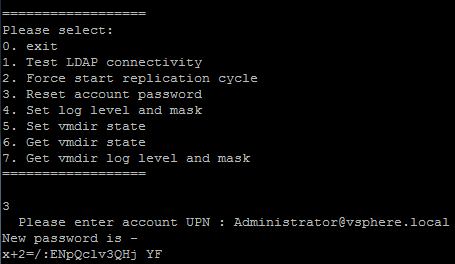
- Start the vdcadmintool
# /usr/lib/vmware-vmdir/bin/vdcadmintool
- Press 3 (Reset account password)
- The tool asks for the Account UPN to reset. Enter Administrator@<DOMAIN> (identified in Step 3)
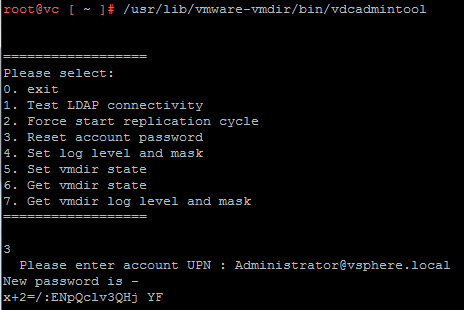
- The tool generates and displays a new password.
- Use the password to log in with the vSphere Web Client and change the password.
Reset ESXi root password with Host Profiles
According to VMware KB1317898, “reinstalling the ESXi host is the only supported way to reset a password on ESXi”. However, there is a loophole as you can set the root password with Host Profiles under certain conditions. This method has two requirements:
- The ESXi hosts needs to be managed by a vCenter
- vSphere Enterprise Plus License is required to use Host Profiles
The vCenter uses a vpxuser to communicate with ESXi hosts, so it does not depend on the root account. As long as the ESXi host is managed by the vCenter, you can change the configuration without knowing the ESXi root password. This method works with all ESXi 5.x and 6.x versions.
- Create a Host Profile with the ESXi you want to reset the root password as reference Host
Web Client > Right-Click the ESXi Host > Host Profiles > Extract Host Profile… - Navigate to the Host Profile and select Actions > Edit Settings…
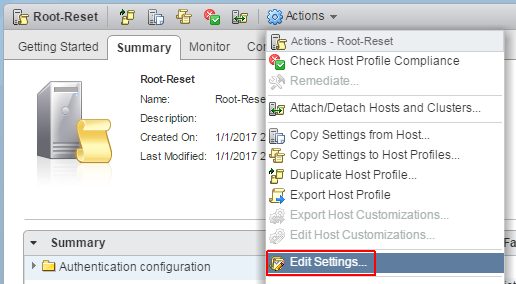
- Navigate to the root User Configuration
Security and Services > Security Settings > Security > User Configuration > root - Set the Password configuration to Fixed password configuration and enter a new password.
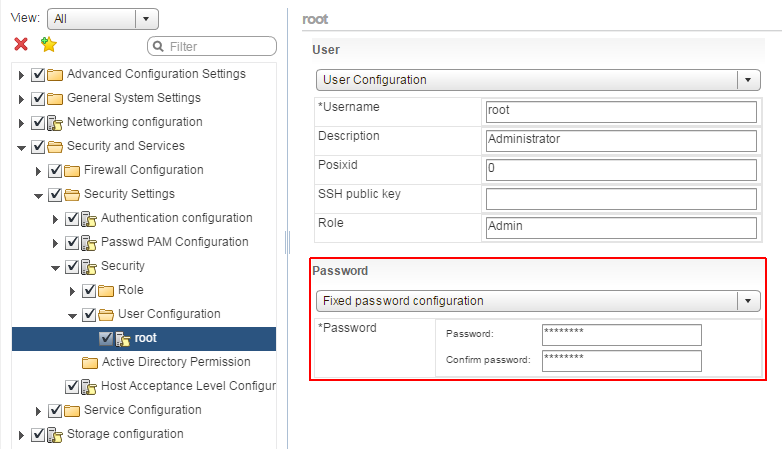
- Click Finish to close the profile configuration
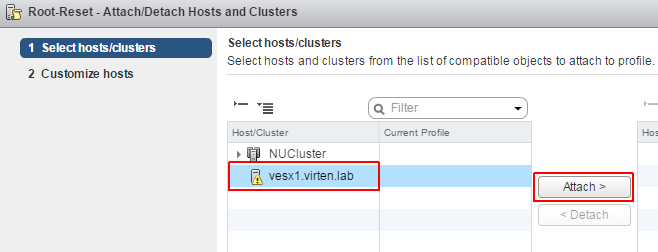
- Right-Click the Host Profile and select Attach/Detach Hosts and Clusters…
- Highlight the ESXi host, Click Attach > and finish the configuration screen
- Put the ESXi host into maintenance mode
- Right-Click the ESXi host and select Host Profiles > Remediate…
- Finish the remediation wizard. The remediation should take less than a minute, no reboot is required.
- Use the new root password to login
Gain Administrative ESXi access with an Active Directory
When you don’t have the Enterprise Plus license, you can join an Active Directory to regain administrative access to the ESXi host. This method circumvents the limitation that root PW recovery is not supported.
- Login to the vCenter with the vSphere Web Client
- Navigate to ESXi > Configure > System > Authentication Services
- Click Join Domain…
- Enter the domain name and user credentials
- Click OK
- In the ESXi configuration, open System > Advanced System Settings
- Enter Config.HostAgent.plugins.hostsvc.esxAdminsGroup in the search field
- Change the settings to match the Administrator group that you want to use in the Active Directory. You can either create a new group in your direcotry or enter an existing group
Reset ESXi root password (Linux Live CD)
When you need to recover root access and the methods above are not applicable, the last method explains how to reset the root password with a Linux Live CD. Please be aware that this method is not supported by VMware as KB1317898 states: “reinstalling the ESXi host is the only supported way to reset a password on ESXi”. You can use any current Linux Live CD or installer CD that has a recovery mode. In this example I’m using Knoppix.
- Shutdown the ESXi host
- Boot the system with the Linux Live CD
- Make sure that you can read the gpt partition table, for example with parted /dev/sda print
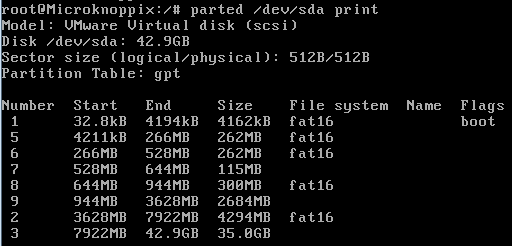
- We are looking for the first fat16 partition with a size of 262MB. IT should be number 5.
- Mount the partition
# mount /dev/sda5 /media/sda5
- Verify that there is a current state.tgz in the directory.
-
# ls -l /media/sda5/state.tgz

- The state.tgz file contains the local.tgz file which contains the configuration. Extract both to a temporary directory.
# cd /tmp/ # cp /media/sda5/state.tgz /tmp/state.tgz # tar -xf state.tgz # tar -xf local.tgz
- Edit the shadow file and remove the root password
# vi etc/shadow
Remove the hashed password until the second colon:

You want a file that looks like this:
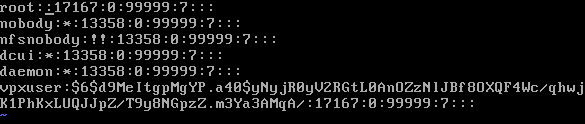
- Save the file and exit the editor (<ESC> :wq <ENTER>)
- Recreate state.tgz with the changed shadow file
# tar -czf local.tgz etc # tar -czf state.tgz local.tgz
- Move state.tgz back to ESXi partition and make sure to overwrite the old file
# mv state.tgz /media/sda5/
- Reboot to ESXi. You should be able to access the DCUI or log in as root without a password.